↳ 2️⃣ ZKP Verifier Network
Our ultimate goal is to enable native verification of Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) within Bitcoin blocks. This advancement requires the introduction of new opcodes—such as OP_verifystarkproof in Bitcoin's script language. We believe that these necessary changes will evolve and be adapted over time, until then we are developing a ZKP Verifier Network.
Building a PoS-Backed ZKP Verifier Network
We are concurrently developing a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) backed Zero knowledge Proof (ZKP) Verifier Network.
This ZKP network functions in the following manner:
-
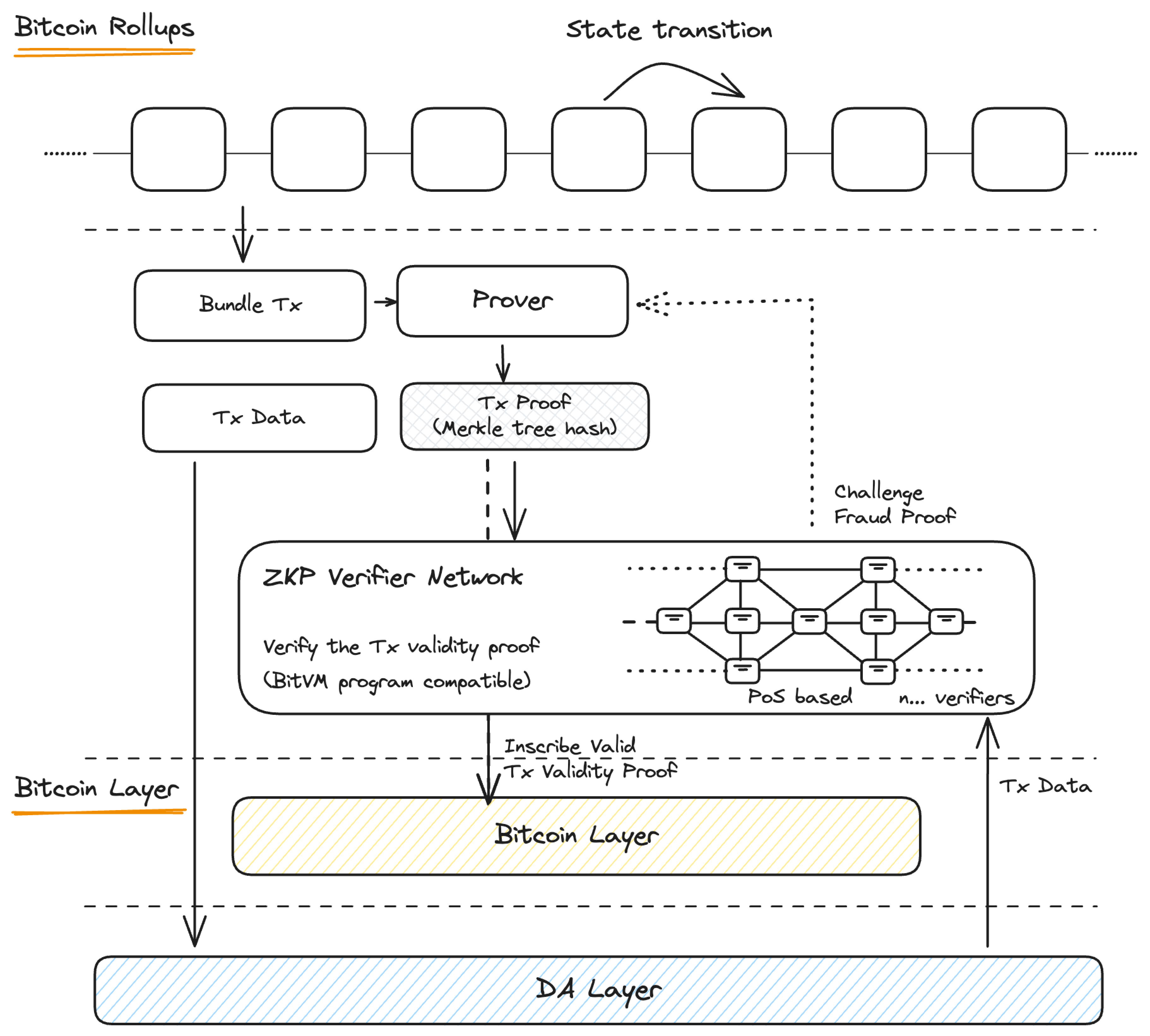
Prover's Role: A prover generates ZK proofs reflecting the state differences of Bitcoin Layer 2, which are then inscribed onto the Bitcoin Layer.
-
Validator's Duty: Proofs submitted to the validator network are meticulously reviewed, and any discrepancies are promptly challenged, ensuring only valid proofs are confirmed and inscribed onto Bitcoin.
The Critical Role of the ZKP Verifier Network
The ZKP verifier network is fundamental in enhancing the security and trust of Layer 2 state transitions. Key roles of the ZKP network include:
-
Ensuring Secure Correctness of L2 State Transitions: By accurately validating the state changes of Layer 2 transactions, the network guarantees their correctness.
-
Decentralizing Trust: The verifier network distributes the trust assumptions associated with validity proofs, mitigating the risks linked to centralized verification processes.
Need for a ZKP Verifier Network
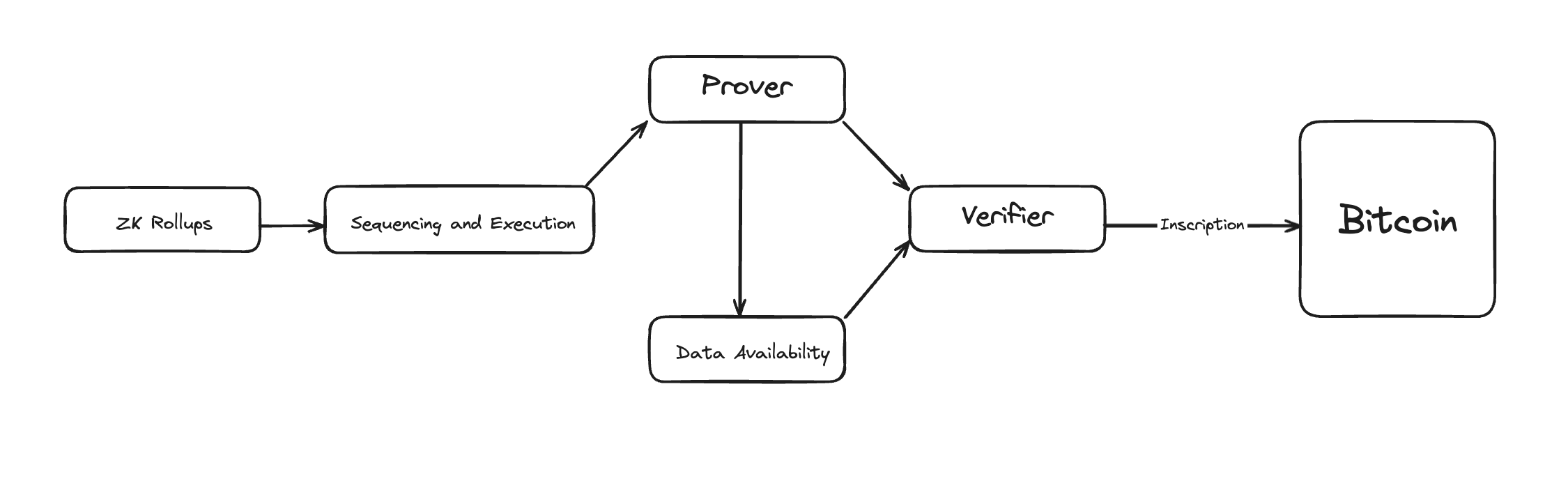
In typical Validium ZK rollup setups, transaction data is pushed to an off-chain data availability layer and publishes zero-knowledge proofs to verify off-chain transactions on Layer 1.
However, the non-Turing-complete nature of Bitcoin's scripting language limits its proof verification capabilities. To address this, our Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP) verifier network ensures that the submitted proofs are compatible, verifiable with BitVM2, and can be natively verified on the Bitcoin Layer.
How the ZKP Verification Happens:
-
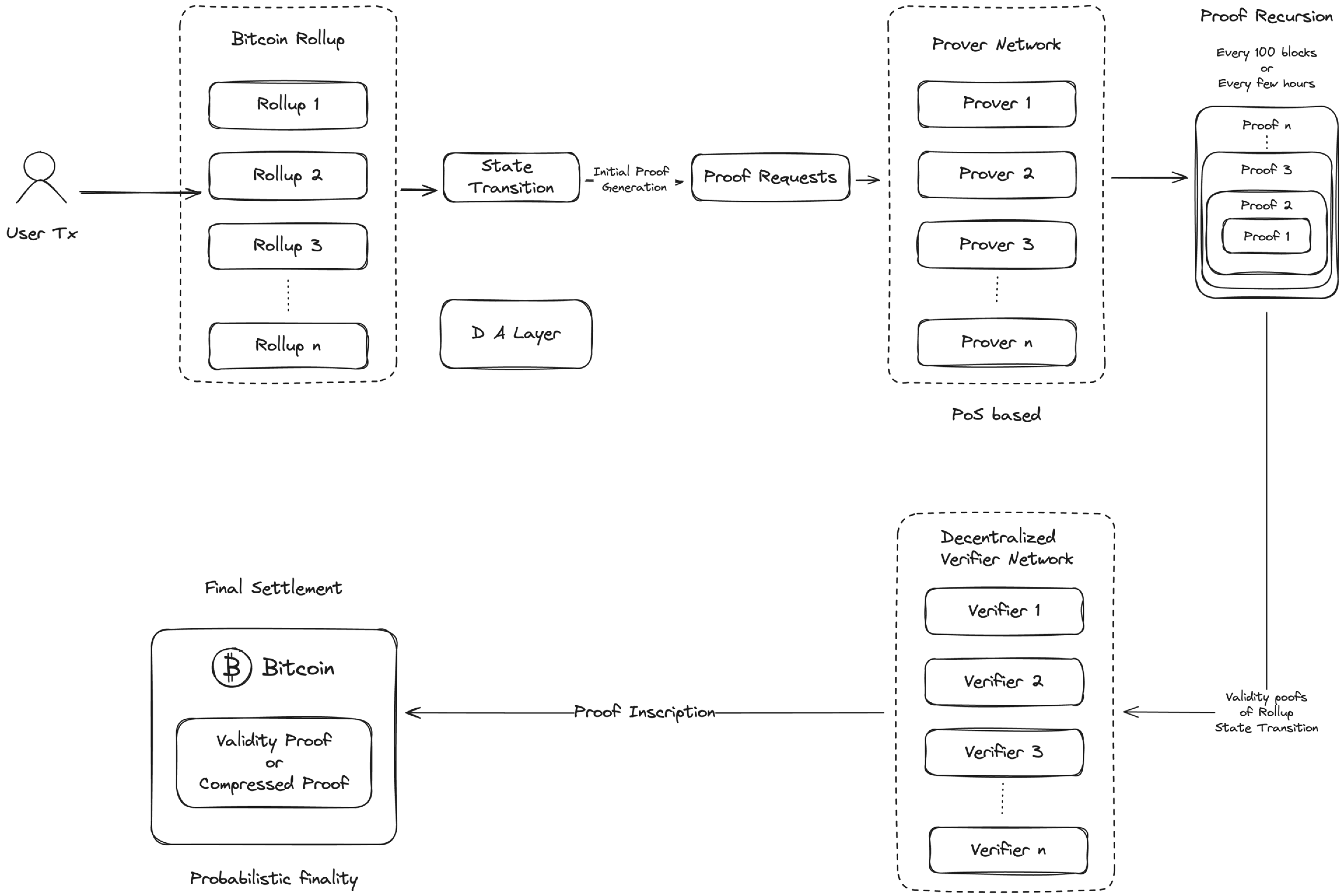
Proof Generation: Bitcoin rollups initiate the process by generating a bundle of transactions on the client side. This bundle is then sent to the Prover Network, a marketplace of provers that generate zero-knowledge proofs for the transactions. These proofs are subsequently compressed using ZK proof recursion and passed to the ZKP Verifier Network.
-
Validation in ZKP Verifier Network: Verifiers in the Proof of Stake (PoS)-backed network consistently monitor for new proofs. When detected, these proofs are gathered and queued for validation. Validators meticulously examine each proof against the claimed state changes. If inconsistencies are detected, a challenge is launched, initiating a secondary verification process to guarantee only valid proofs are accepted. This process leverages ZK-Stark along with the instruction set of RISC-V as used in Zero-Knowledge Virtual Machine (ZKVM) for efficient and scalable validation.
-
Decentralized Verification: The decentralized verifier network consists of validator nodes and guardian nodes. Proof recursion can occur every 100 blocks or every few hours, after which the proofs are verified within the network.
-
Final Settlement: Once verification is complete, the aggregated proof or the validity proof is inscribed into the Bitcoin blockchain, ensuring final settlement.
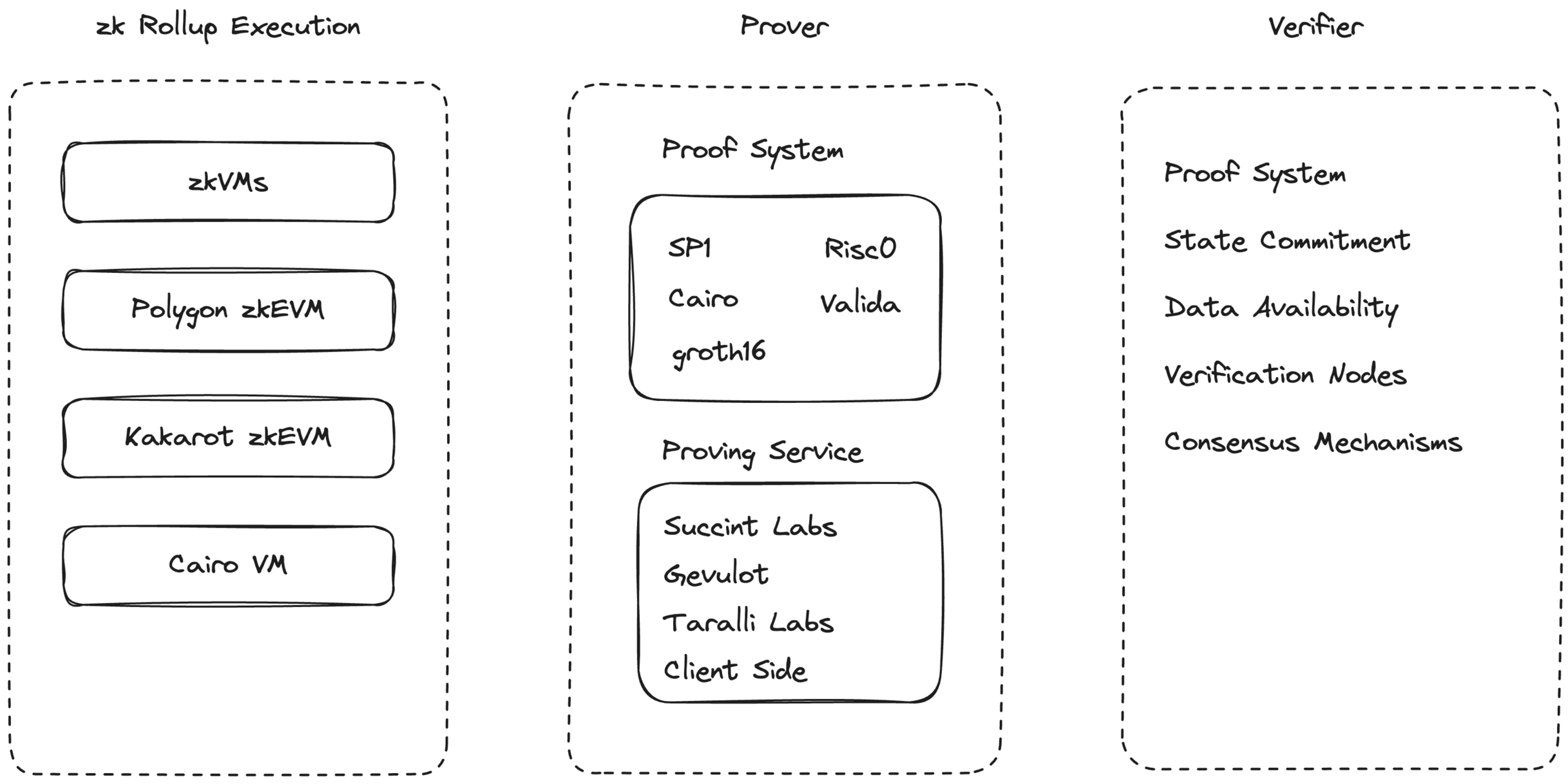
Reviewing zkVMs and Their Components:
As part of our ZKP verification layer, we are actively reviewing various zkVMs (Zero-Knowledge Virtual Machines) and their components
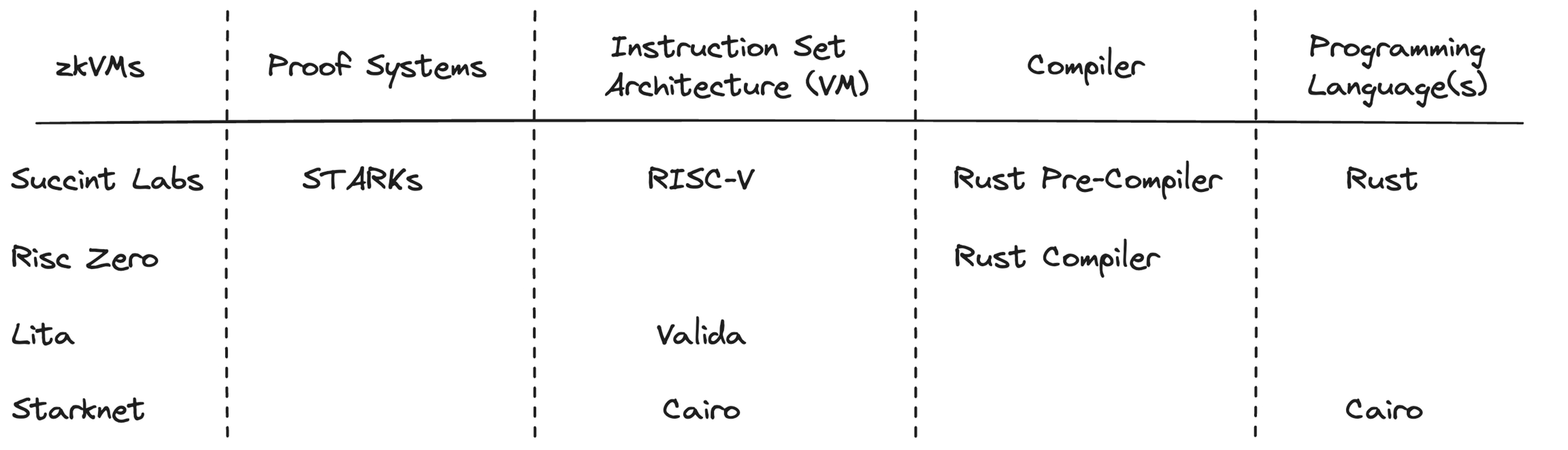
For integration we are particularly reviewing the prover & verification component to facilitate the zk Rollup execution
Future Roadmap also includes using BitVM for On-Chain Verification
With BitVM Program, we have the capability to verify validity proofs directly on the Bitcoin layer. Leveraging BitVM, we are exploring a framework that iteratively fetches ZK proofs from Bitcoin blocks and authenticates these proofs. This process ensures the integrity and finality of state differences in Layer 2 networks. But BitVM is still under development and needs lot of work before ready.

